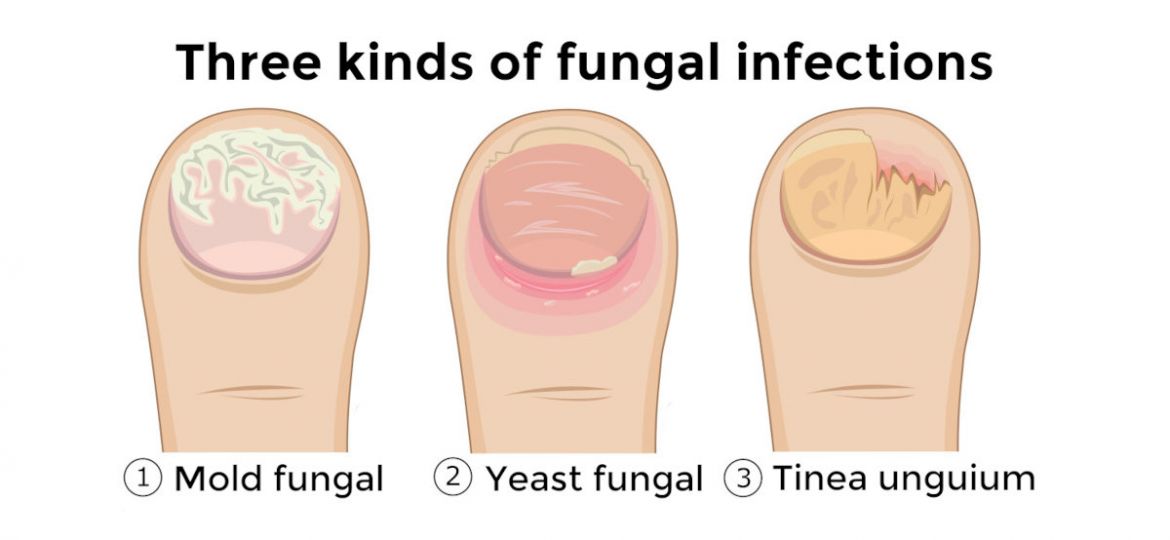
What are the Types of Toenail Fungus?
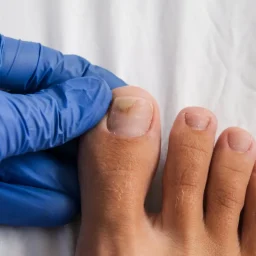
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, includes several types of fungal nail infections. The most common type is distal subungual onychomycosis, which often starts at the tip of the nail and spreads inward, causing discoloration and thickening. White superficial onychomycosis is another common type, characterized by white spots or patches on the nail surface, which can become crumbly and brittle over time.
Proximal subungual onychomycosis is a less common type of fungal infection that begins at the base of the nail near the cuticle and spreads outward. This type is more likely to occur in individuals with compromised immune systems. These infections can affect both fingernails and toenails, though toenails are more commonly affected due to the warm, moist environment inside shoes.
Fungal nail infections often accompany athlete’s foot, a fungal infection of the skin on the feet, and can spread through direct contact or by using contaminated nail clippers. Prevention includes keeping nails clean and dry, wearing breathable footwear, and avoiding shared nail care tools. Treating different types of nail fungus infections promptly is important to prevent further nail damage and potential spread of the infection. If over-the-counter treatments are ineffective, consulting a healthcare professional for prescription medication or other treatments is advisable.
What are Bacterial Fungal Infections in Toenails? What are the Causes?
A bacterial fungal infection in toenails, also known as a mixed infection or co-infection, involves the simultaneous presence of both bacterial and fungal pathogens affecting the toenails. This condition can lead to more severe symptoms and complications compared to infections caused by either bacteria or fungi alone.
Causes of Bacterial Fungal Infections in Toenails:
- Poor Foot Hygiene: Inadequate foot hygiene, such as not drying feet properly after bathing or wearing damp socks and shoes, creates a conducive environment for both bacterial and fungal growth.
- Skin Trauma: Any injury to the toenails or surrounding skin, such as cuts, abrasions, or ingrown toenails, can provide entry points for bacteria and fungi to infect the nails.
- Warm and Moist Environment: Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, which are often found in closed-toe shoes, especially if worn for extended periods without proper ventilation.
- Immune System Weakness: Individuals with compromised immune systems due to conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapies, are more susceptible to bacterial fungal infections.
- Shared Footwear and Tools: Sharing shoes, socks, or nail grooming tools with someone who has a fungal or bacterial infection can lead to cross-contamination and the development of mixed infections.
- Existing Nail Infections: Pre-existing fungal infections of the toenails (onychomycosis) can weaken the nail structure, making it more vulnerable to bacterial invasion and co-infection.
- Antibiotic Use: Prolonged or frequent use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms on the skin and nails, leading to opportunistic infections by both bacteria and fungi.
Symptoms of Bacterial Fungal Infections in Toenails:
- Discoloration of the toenail, such as yellowing, darkening, or a greenish hue.
- Thickening or distortion of the nail shape.
- Brittle, crumbly, or flaky toenails.
- Foul odor emanating from the infected toenail.
- Pain, tenderness, or discomfort around the nail bed.
- Skin around the area may exhibit redness, swelling, or inflammation.
Understanding the Stages of Toenail Fungus Progression
As a podiatrist at Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, I frequently see patients who could have avoided severe complications by understanding how toenail fungus progresses through distinct stages. Recognizing these stages early allows for more effective treatment and prevents the infection from spreading to other nails or causing secondary health issues.
Stage 1: Early Infection – The Window of Opportunity
In the initial stage of toenail fungus, patients typically notice subtle changes that are easy to dismiss. The infection often begins with a small white or yellow spot under the tip of the nail or along the sides where fungi can more easily penetrate. During this early stage, you may observe slight discoloration, minor nail thickening, or small white patches on the nail surface. The nail may also begin to feel slightly different in texture, becoming somewhat brittle or developing tiny cracks. This stage presents the best opportunity for treatment, as the infection hasn’t yet penetrated deeply into the nail bed or spread to surrounding areas. Many patients mistake these early signs for minor nail damage or aging, but prompt evaluation by a podiatrist can prevent months of more intensive treatment later.
Stage 2: Moderate Progression – When Symptoms Become Noticeable
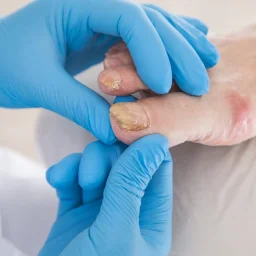
As the infection progresses to the moderate stage, the discoloration becomes more pronounced, with nails turning yellow, brown, or developing a greenish hue. The affected nail continues to thicken significantly, and you may notice changes in the nail’s shape or texture. At this stage, the nail may become thick enough to cause discomfort when wearing shoes or during physical activities. The fungus spreads deeper into the nail bed and may begin affecting adjacent nails through direct contact or shared footwear. Patients often report a foul odor emanating from the infected nail, and the nail may start to separate from the nail bed, creating gaps where debris can accumulate. This stage requires more aggressive treatment approaches, as over-the-counter remedies are typically insufficient to penetrate the thickened nail structure effectively.
Stage 3: Advanced Infection – Total Dystrophic Onychomycosis
In the final stage, known as total dystrophic onychomycosis, the infected nail becomes severely thick, brittle, and may begin to detach from the nail bed entirely. The nail plate becomes elevated and misaligned as the infection reaches this chronic stage, often requiring more intensive medical intervention. At this advanced stage, the nail may crumble when touched, and walking can become uncomfortable or painful. In severe cases, the fungal infection can spread to surrounding skin and other nails, potentially leading to secondary bacterial infections. Treatment at this stage typically requires prescription oral antifungal medications, which may need to be taken for three to four months for toenails. The healing process can take 12 to 18 months as healthy nail growth must completely replace the damaged tissue from the base of the nail outward. Some patients may require nail removal or surgical intervention if the infection doesn’t respond to conservative treatment, making early detection and treatment crucial for maintaining long-term nail health.
Prevention of the various types of nail fungus
Preventing toenail fungus, also known as tinea unguium or onychomycosis, involves adopting good foot hygiene practices and minimizing risk factors that contribute to fungal infections of the nail. Here are effective ways to prevent toenail fungus:
- Maintain Good Foot Hygiene: Keep your feet clean and dry, especially after bathing or swimming. Ensure thorough drying between toes and use talcum powder to absorb excess moisture.
- Wear Breathable Footwear: Opt for shoes made of breathable materials like leather or mesh to allow proper ventilation and reduce moisture buildup.
- Change Socks Regularly: Wear clean, dry socks made of moisture-wicking materials and change them daily, especially if your feet tend to sweat excessively.
- Opt for Properly Fitting Shoes: Wearing shoes that fit well helps prevent the warm, moist conditions that encourage fungal growth. Choose shoes with enough room for your toes to move comfortably.
- Practice Proper Nail Care: Trim your toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short to prevent ingrown nails, which can create entry points for fungal infections.
- Protect Your Feet in Public Areas: Wear sandals or protective footwear in communal showers, locker rooms, and pool areas to reduce the risk of picking up fungal infections.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Refrain from sharing socks, shoes, towels, or nail clippers with others to prevent the spread of fungal infections.
- Manage Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or a weakened immune system can increase susceptibility to nail fungus. Seek professional healthcare guidance to effectively manage these conditions.
- Be Cautious with Nail Salons: Ensure that nail salons follow proper hygiene practices and sterilize their tools to avoid fungal contamination during pedicures.
If you suspect a fungal infection of the nail, such as white or yellow discoloration, thickening, or crumbling of the nail, seek prompt medical attention. Treatment options include topical or oral antifungal medications prescribed by a healthcare provider, proper nail-trimming techniques, and lifestyle modifications to prevent a recurrence. Consistent preventive measures and early detection can significantly reduce the risk of toenail fungus and maintain healthy nails.
Treatment of Nail Fungus
Medical treatment options for toenail fungus may vary depending on the severity and type of infection. Here are several common medical treatments prescribed by healthcare providers:
1. Topical Antifungal Medications: These medications come in the form of creams, ointments, or nail lacquers that are applied directly to the infected toenail and surrounding skin. Examples include terbinafine cream, ciclopirox nail lacquer, and efinaconazole solution. Topical treatments are often used for mild to moderate cases of toenail fungus.
2. Oral Antifungal Medications: For more severe or stubborn infections, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. These medications, such as terbinafine (Lamisil), itraconazole (Sporanox), and fluconazole (Diflucan), work systemically to target fungal infections throughout the body, including the toenails. Oral antifungals are typically taken daily for several weeks to months, depending on the extent of the infection.
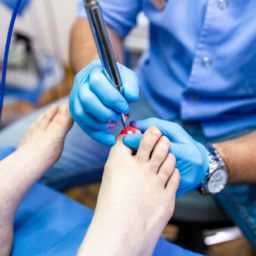
3. Surgical Nail Removal: In cases where the toenail fungus is severe, causing pain, deformity, or not responding to other treatments, surgical removal of the infected nail may be recommended. This procedure involves numbing the toe with a local anesthetic and surgically removing the affected nail to allow a new, healthy nail to grow in its place.
4. Laser Therapy: Laser fungal treatment for all types of nail fungus is a newer option that involves using a laser device to target and destroy the fungal infection in the toenail nail bed without harming surrounding tissues. This treatment may require multiple sessions and is often used in conjunction with other therapies.
5. Combination Therapy: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend a combination of topical and oral antifungal medications, along with other treatments like nail debridement (removing damaged nail tissue) or periodic monitoring of the infection’s progress.
It’s important to follow the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider and complete the full course of medication, even if the symptoms improve before finishing the treatment. Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor the progress of the toenail fungus and adjust treatment as needed.
When to See A Podiatrist
At Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, our dedicated team of experts takes a comprehensive approach to managing various types of nail fungus on your toes. We begin with a thorough and accurate diagnosis to understand the specific type and severity of the fungal infection. Our experienced podiatrists then tailor personalized treatment plans, utilizing the latest advancements in antifungal therapies to effectively target and eliminate the fungus.
Beyond treatment, we emphasize ongoing support and education to promote foot health and prevent recurrence. Our team provides valuable guidance on proper foot care practices, including hygiene tips and footwear recommendations to create an environment that discourages fungal growth. We understand the impact toenail fungus can have on your overall well-being, and our goal is to provide compassionate care and comprehensive solutions. To take the first step towards healthier, fungus-free nails, schedule an appointment with Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists today.
Whether you’re in Fort Lauderdale or Palm Harbor, expert podiatry care is just a call or click away. Contact us at 954-561-3338 or click the link below to schedule your visit.