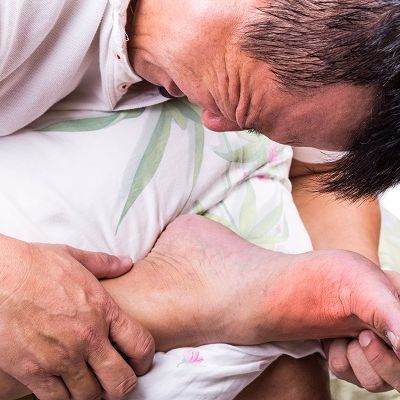
Diganosis and Treatment Of Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that often attacks the foot and ankle. Symptoms include severe pain, redness and swelling around the effected joint with no history of injury or inciting event. Gout is caused by the buildup of uric acid in the blood. The uric acid is a break down product of certain proteins, called purines which are found in foods like red meet, shell fish, cheese, wine and beer – All the good stuff! That’s why Gout is sometimes referred to as “The Disease of Kings”.
DIAGNOSIS OF GOUT
The diagnosis of gout may be made by a blood test showing elevated levels of uric acid, a joint fluid analysis confirming the presence of uric acid crystals, or in advanced cases, an x-ray showing a particular type of erosion around the joint.
Symptoms of Gout In Foot
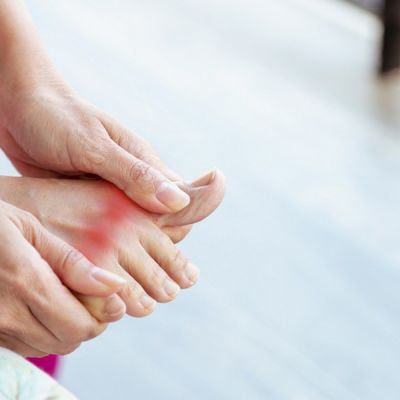
The most common signs and symptoms of gout in the foot include sudden and severe pain, redness and swelling in the affected joint, stiffness and tenderness in the joint, and a high fever. These symptoms are usually accompanied by warmth and redness in the affected area and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. In some cases, gout can also cause a rash or small lumps to form on the skin near the affected joint.
As you know, the big toe, also known as the hallux, is the first toe on the foot. It is the largest and most important toe for balance and movement, as it helps with walking and standing. However, this big toe joint is also a common site for gout attacks, which can cause severe pain, redness, and swelling. Other common conditions that can affect the big toe include bunions, hammertoes, and ingrown toenails. Injuries such as sprains and fractures can also occur in the big toe. It is important to take care of the big toe and seek medical attention if you experience any pain or discomfort in this area.
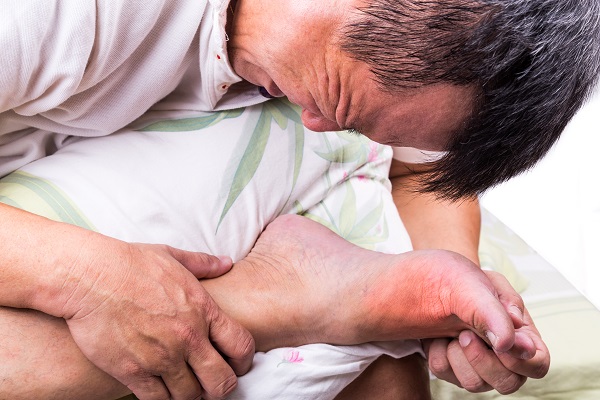
Gout Treatment In Foot
Treatment for gout in the foot typically involves reducing the inflammation and pain in the affected joint and preventing future gout attacks. The following are some common treatment options for gout in the foot:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Colchicine, a medication specifically for gout, can also be used to reduce inflammation and prevent future attacks.
- Corticosteroids: Injections of corticosteroids, such as prednisone, into the affected joint can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Lifestyle changes: Changing certain lifestyle habits, such as losing weight, reducing alcohol consumption, and limiting the intake of foods high in purines, may help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Surgery: In severe cases of gout, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged joint tissue and replace it with an artificial joint.
It is important to consult a rheumatologist or a podiatrist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, as gout can also be mistaken for other conditions.
Treatment for chronic gout is primarily focused on reducing the intake of purines in the diet, reducing the formation of uric acid from proteins, and/or helping your body to excrete more uric acid. This can be done by taking oral medicine. Acute gout attacks are treated with anti-inflammatory medicine, heat, or corticosteroid injections into the effected joint. Repetitive gout should be treated with a combination of diet and with oral medication.
GOUT
Foot and ankle surgery is a highly specialized area of medicine. If you were someone you know is experiencing pain in the foot ankle or lower leg, it is imperative that they see a specialist. The podiatrists at Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists provide the most technologically advanced diagnostic modalities and treatment options for your ankle problems available in the area, as well as free transportation for existing patients who have difficulty driving due to foot or ankle pain.