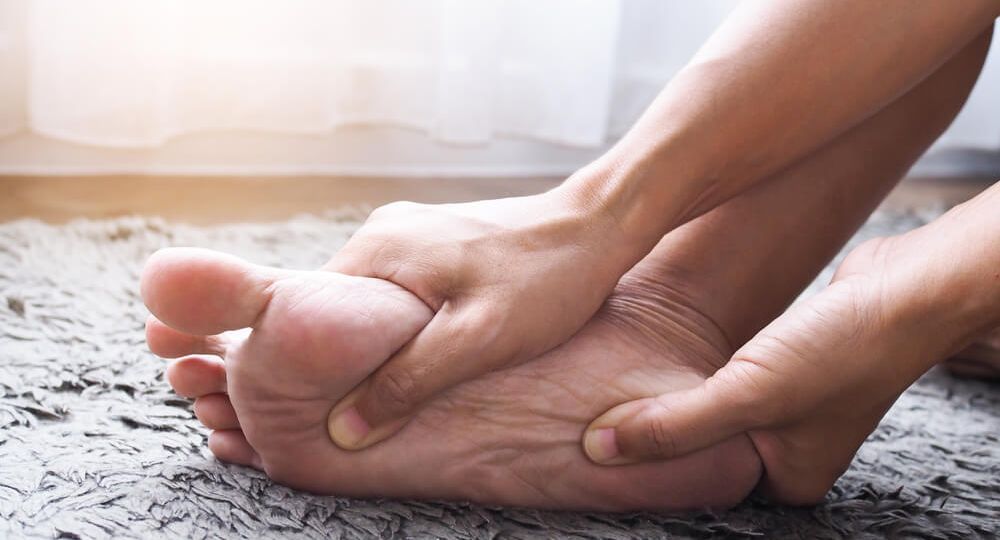
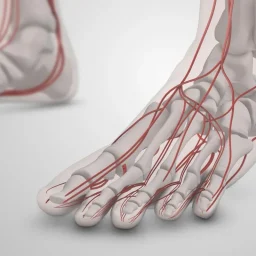
More than 20 million people in the United States suffer from peripheral neuropathy and nerve pain according to the National Institute of Health. Neuropathy describes a class of disorders arising from an injury to a nerve. Peripheral neuropathy involves the nerves in the arms and legs with symptoms often presenting in the hands and feet. One or more nerves may be involved and symptoms can present differently in each case. Most people describe the symptoms as numbness, burning, tingling and temperature changes. There are many potential causes for neuropathy as well as treatment including medication, injections and surgery.
Symptoms
Peripheral neuropathy often presents gradually with numbness, tingling, burning and sometimes weakness and loss of balance. Many people feel they are wearing an extra sock or feel like their feet are like cardboard. Most symptoms are worse at night and interfere with daily activities and sleep. In advanced stages, muscles atrophy and create weakness in the legs. Skin also presents with changes such as dry and cracking, as those nerves that control sweating become affected.
Causes
The most common cause for peripheral neuropathy and nerve pain in the United States is diabetes mellitus. The increased blood sugar levels lead to nerve damage and the neuropathy symptoms typically start in the toes. People with diabetes may notice their symptoms improve as their blood sugar levels improve.
- Radiculopathy or nerve injury in the spine is often a cause for neuropathy in the legs and feet. Symptoms can also coincide with lower back pain or injury and may need further evaluation and possible treatment of that area.
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome often lead to peripheral neuropathy as the body attacks the nerve tissue.
- Alcoholism is a common cause for peripheral neuropathy as the chronic exposure to alcohol damages the nerves.
- Chemotherapy drugs often cause neuropathy that only improves minimally once therapy finishes.
- A majority of idiopathic neuropathy, where there is not a specific underlying cause of the condition, is very common in patients over the age of 60. This can lead to increased risk of falls and decreased levels of activity due to pain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing neuropathy and nerve disorders involves evaluating for an underlying cause and assessing the type of neuropathy present.
- Bloodwork and urinalysis are often performed.
- Nerve Conduction Velocity studies are helpful with Electromyography to assess the level of nerve damage as well as the type of nerve damage.
- Lumbar puncture and spinal tap procedures may be necessary.
- Nerve biopsies and skin biopsies are a minimally invasive way to sample the area of concern to determine if nerves are responding to treatment.
Prevention
Ways to prevent peripheral neuropathy involve regular visits to the doctor to screen for medical conditions, like diabetes, that can cause nerve damage. By exercising and healthy eating people can improve circulation and nerve health. Regular blood work is important for monitoring vitamin B levels and checking for other imbalances that can lead to neuropathy. For vegetarians, vitamin B12 needs to be added to their diet to prevent nerve issues. There are many supplements on the market claiming to cure neuropathy but it is always best to ask your doctor for the recommended supplement that is right for you.
Treatment For Peripheral Neuropathy And Nerve Pain
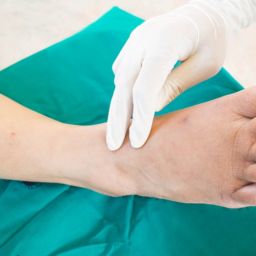
Treatment for neuropathy in the legs and feet is aimed at treating the underlying cause to slow progression as well as alleviate symptoms and protect insensate areas.
- Oral medications as well as topical medications have been effective for neuropathic pain.
- CBD oil used topically or as a tincture
- Anodyne light therapy along with physical therapy for balance
- Amniotic fluid injections around the areas of nerve compression to decrease inflammation
- STIMWAVE therapy is a cutting-edge treatment for neuropathy that is an alternative to surgery for chronic neuropathic pain.
- Surgery for compression nerves and neuropathy is performed when conservative measures fail. The procedure of peripheral nerve decompression surgery is a minimally invasive, outpatient procedure with minimal downtime that provides excellent results for many different types of neuropathy.
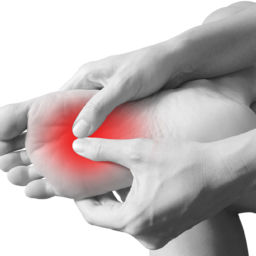
Neuroma
Do you feel like you have a pebble in your shoe? It could be a neuroma. A Morton’s neuroma is an irritation of a nerve in the foot that produces pain with activity and certain shoes. Pain in the ball of the foot could also be neuropathy in the feet so an accurate diagnosis is important. Imaging and nerve studies are used for diagnosis and treatment may include orthotics, padding, injections or surgery. Injections of cortisone and alcohol are traditionally used to decrease inflammation. New and innovative injections with amniotic fluid have provided excellent results without harsh chemicals. Surgery for neuroma pain is a last resort that involves decompressing and sometimes removing the painful abnormal nerve branch.
If you suffer from neuropathy or nerve pain without relief from conventional treatment you should set up an evaluation to see what other treatment options are available for your condition to get you back to activity with less pain.
By Dr. Ashley Bowles, DPM, FACFAS
Certified Foot and Ankle Specialist – Boca Raton, Florida[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]