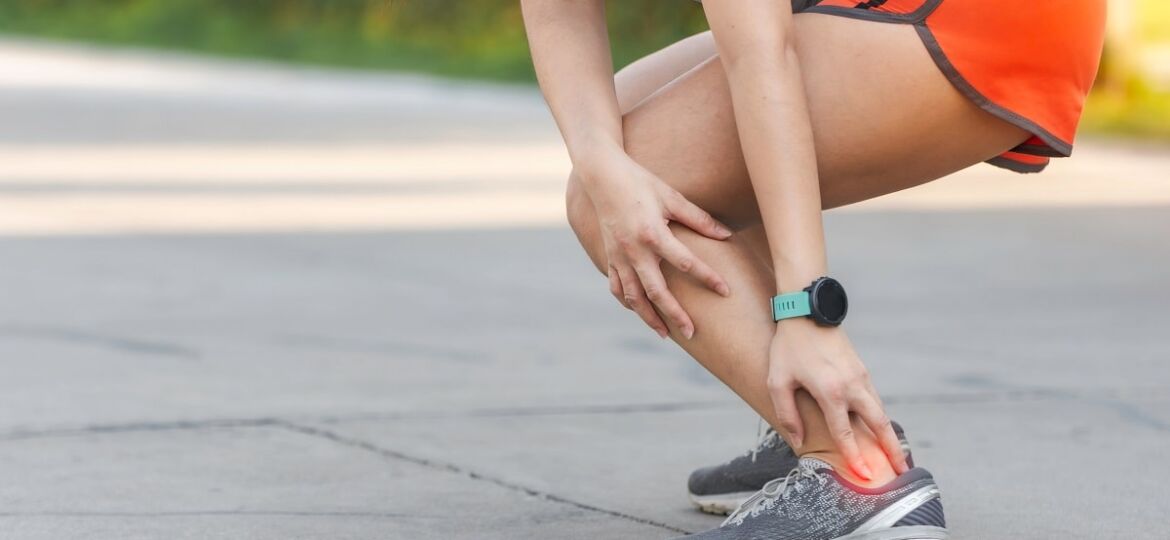
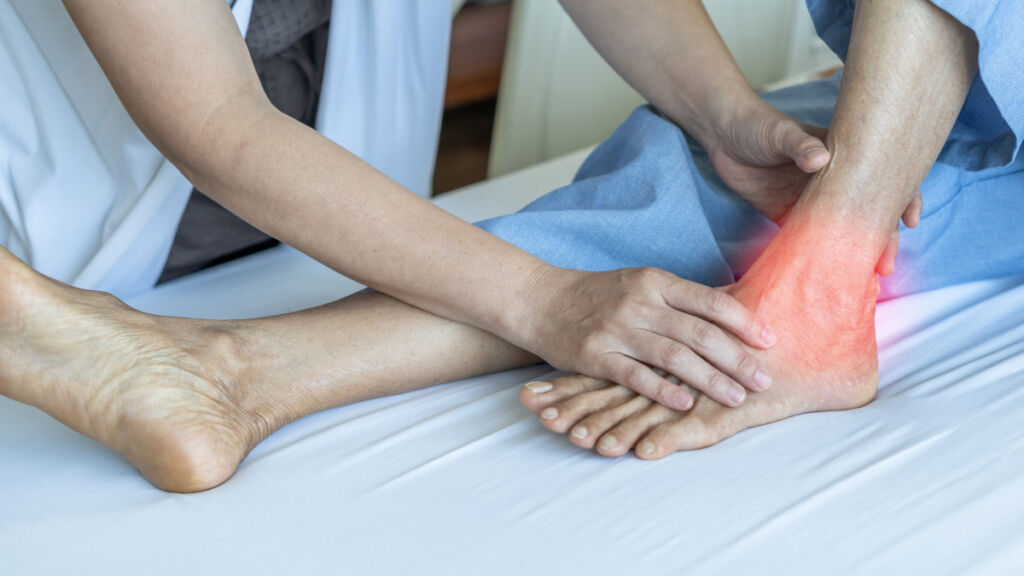
Are you experiencing pain on the inside of your ankle or foot? Does it get worse with physical activity or standing for long periods? If your answers to these questions are “yes”, then you might be suffering from posterior tibial tendonitis. This condition can cause discomfort and limit your mobility, affecting approximately 3% of the population. But with the right treatments and management, you can find relief and get back to your daily activities.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Anatomy
Before diving into the various treatment options available for posterior tibial tendonitis, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the intricate anatomy of this specific tendon.
The posterior tibial tendon, originating from the inner side of your calf muscle, extends down to the bones located on the inner part of your foot. Its primary role revolves around providing essential support to the arch of your foot and facilitating the regulation of inward movement in your ankle joint. This remarkable tendon plays a pivotal role in numerous weight-bearing activities, including walking, running, and engaging in other physically demanding endeavors.
By appreciating the intricate details of this tendon, we gain a deeper understanding of its significance and the importance of proper care and treatment when it comes to addressing posterior tibial tendonitis.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis Symptoms
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is characterized by several tell-tale symptoms that primarily affect the foot and ankle.
- One of the earliest signs of this condition is pain in the inner part of the foot and ankle, which can become more pronounced during physical activities like running or walking. As the tendon becomes more damaged, individuals may experience an increasing discomfort that can extend to the outer ankle.
- In addition to pain, swelling around the ankle joint is another common symptom. This can be accompanied by redness and a warm sensation in the affected area.
- As the condition progresses to later stages, the arch of the foot may begin to collapse, leading to adult-acquired flatfoot. This often results in an alteration in the individual’s gait, making it difficult to stand, walk, or run.
- Another noticeable symptom is the inability to stand on the toes of the affected foot, especially in more advanced cases. It’s crucial to pay attention to these signs as early detection can significantly improve the outcome of posterior tibial tendonitis treatments. Always consult with certified foot and ankle specialists if you experience any of these symptoms.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Without proper treatment, there are chances that posterior tibial tendonitis can progress to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). This is a more serious condition where the tendon becomes damaged and weakened, leading to flat feet or fallen arches. This can result in a loss of arch support and stability, making it difficult to perform activities that require standing or walking for prolonged periods.
In addition to flat feet, PTTD can also cause pain and swelling on the outside of the ankle due to overcompensation by other muscles in the foot, as they try to compensate for the weakened posterior tibial tendon. It is important to seek treatment and address the issue early on to prevent further complications and maintain proper foot function.
Stages of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Posterior tibial tendonitis can be categorized into four stages based on the severity and progression of symptoms.
- In the initial stages, there might be mild pain and swelling, without any visible alteration in the foot structure.
- As it advances, the foot’s arch may gradually flatten, accompanied by intensified pain.
- In severe cases, the tendon can completely rupture, resulting in significant disability and walking difficulties.
Treatment for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
The treatment for posterior tibial tendonitis depends on the stage of the condition.
- In the early stages, rest and anti-inflammatory medication can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Wearing a walking boot or short leg cast can also provide support to the affected foot while it heals.
- Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the affected calf muscles and support the arch of the foot.
- In some cases, orthotic shoe inserts may be prescribed to provide additional arch support and prevent overpronation.
If the condition has progressed to a more severe stage or does not respond to conservative treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. The type of surgery will vary depending on the extent of damage to the tendon. In cases where there is a partial tear, the surgeon may simply remove the damaged part of the tendon and repair it. For complete tendon ruptures, a graft may be used to replace the missing portion of the tendon.
Physical Therapy for Rehabilitation
After surgery or during the later stages of posterior tibial tendonitis, physical therapy can play a crucial role in rehabilitation. Our surgeons are Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists who can design a personalized exercise program to help strengthen the affected tendon and surrounding muscles. These exercises may include stretching, range of motion activities, and strengthening exercises. It is essential to follow the physical therapy plan diligently to ensure proper healing and prevent future injuries.
Conclusion
Posterior tibial tendonitis can be a challenging condition that can significantly impact one’s daily life. However, with proper treatment and care, it is possible to manage the symptoms and prevent further damage to the tendon. Remember to listen to your body and seek medical attention if you experience any pain or discomfort in your foot and ankle area. With the help of certified foot and ankle specialists, you can overcome this condition and get back on your feet in no time. Should your condition deteriorate, do not hesitate to consult with our dedicated team of foot doctors at Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists. We are committed to restoring your mobility and getting you back on your feet.
Our offices offer flexibility to patients, so there is less suffering to endure. Feel free to make an appointment with us on weekdays after hours or even on Saturdays. To make an appointment with our specialists, give us a call today at (855) 550-3338.