*About the Author: Dr. Kyle Kinmon ,DPM, MS, FACFAS
This article was reviewed by a board-certified podiatrist with over 15 years of experience in diagnosing and treating foot and ankle conditions. Our practice specializes in comprehensive foot care, from common conditions like tendonitis to complex surgical interventions.
Nearly 85% of diabetes-related amputations begin with a foot ulcer that becomes infected. Yet most of these devastating outcomes are preventable with early recognition and proper care.
At Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, our team of board-certified podiatrists across multiple locations has dedicated decades to helping patients with diabetes protect their feet and avoid serious complications. We’ve seen firsthand how knowledge and prompt action can make the difference between a minor issue and a life-changing outcome.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection saves limbs: Recognizing signs of diabetic foot infection early—including redness, warmth, swelling, or drainage—can prevent serious complications and reduce amputation risk by up to 85%
- Daily foot inspections are critical: People with diabetes should examine their feet every day for cuts, blisters, or color changes, as peripheral neuropathy can mask pain signals
- Prompt medical attention is non-negotiable: Any signs of infection require immediate professional evaluation, as diabetic foot infections can progress rapidly within 24-48 hours
- Comprehensive treatment approach works best: Successful management combines antibiotic therapy, proper wound care, blood sugar control, and often specialized footwear or offloading devices
- Prevention is achievable: Following a structured foot care routine, maintaining good blood sugar levels, and regular podiatric check-ups can prevent most diabetic foot infections
Understanding a Diabetic Foot Infection
A diabetic foot infection occurs when bacteria enter the skin through a wound, ulcer, or break in the foot’s protective barrier. For individuals with diabetes, these infections pose particularly serious risks due to several interconnected factors that compromise the body’s natural healing and defense mechanisms.
According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America, diabetic foot infections represent one of the most common complications requiring hospitalization among people with diabetes. These infections can range from superficial skin involvement to deep tissue infections affecting muscles, tendons, and bone.
Why Diabetes Increases the Risk
Several physiological changes associated with diabetes create a perfect storm for foot infections:
Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy damages the nerves in your feet, reducing sensation and your ability to feel pain, temperature, or pressure. This means you might not notice a small cut, blister, or injury that becomes infected. Our physicians regularly see patients who have walked on severe ulcers for days without realizing the extent of their injury.
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Diabetes damages blood vessels over time, leading to peripheral vascular disease. Reduced blood flow means less oxygen and fewer white blood cells reach your feet to fight infection and promote wound healing. This compromised circulation also limits the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy, as medications cannot reach infected tissue in adequate concentrations.
Impaired Immune Response
Elevated blood sugar levels impair white blood cell function, reducing your body’s ability to fight bacterial infections effectively. High glucose also creates an environment where bacteria thrive, further increasing infection risk.
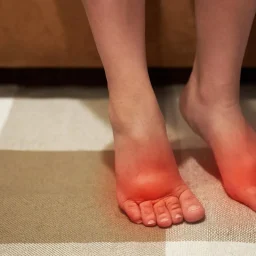
Recognizing Signs of Diabetic Foot Infection
Early identification of infection is crucial for successful treatment. Watch for these warning signs:
Visible Signs:
- Redness, warmth, or swelling around a wound or ulcer
- Drainage or pus from any opening in the skin
- Foul odor from the affected area
- Discoloration or darkening of skin tissue
- Visible bone or deep tissue through an ulcer
Systemic Symptoms:
- Fever or chills indicating systemic infection
- Elevated blood sugar levels that are difficult to control
- Fatigue or general feeling of illness
- Loss of appetite
Advanced Warning Signs:
- Black or necrotic (dead) tissue
- Spreading redness up the leg
- Rapid progression of symptoms within hours
- Severe pain (even with neuropathy, severe infections can cause pain)
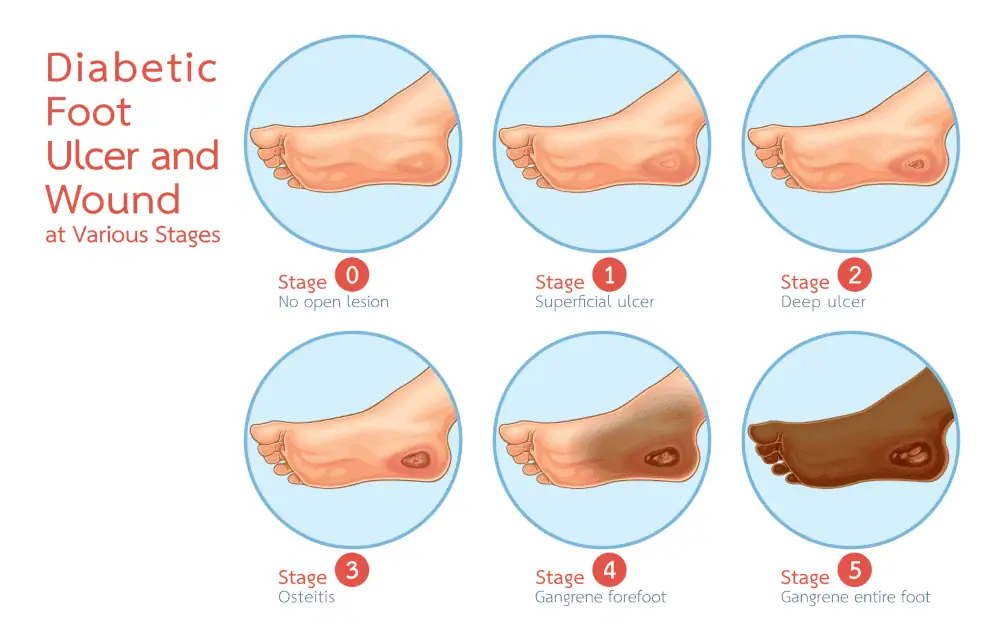
Classification and Severity Assessment
Our specialists classify diabetic foot infections based on severity to guide treatment decisions:
Mild Infections: Involve only skin and subcutaneous tissue with minimal systemic signs. These typically present with localized redness and swelling extending less than 2 centimeters from the wound edge.
Moderate Infections: Extend deeper into tissues or show more extensive cellulitis. Patients with diabetic foot infections at this stage may have systemic inflammatory response but remain clinically stable.
Severe Infections: Involve deep tissue, bone, or show signs of systemic toxicity. These cases often require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotic therapy and possible surgical intervention.
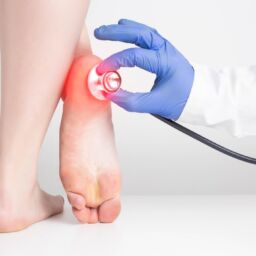
 Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach
Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach
Accurate diagnosis guides effective treatment. Our evaluation includes:
Physical Examination
Our podiatrists thoroughly inspect the foot, assess circulation through pulse checks, evaluate sensation using monofilament testing, and probe any wounds to determine depth and the presence of exposed bone or foreign body.
Laboratory Testing
Blood work including white blood cell count, inflammatory markers, and blood glucose levels helps assess infection severity and overall metabolic control. Wound cultures guide appropriate antibiotic selection.
Imaging Studies
Plain X-rays often serve as the initial imaging study to identify bone involvement, foreign bodies, or gas in tissues. When X-rays are inconclusive, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed visualization of deep tissue infection and osteomyelitis (bone infection).
Advanced imaging helps distinguish between Charcot arthropathy and osteomyelitis, two conditions that can appear similar but require very different treatment approaches.
Bone Biopsy
In cases where osteomyelitis is suspected, bone biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosis. This procedure provides both culture information for targeted antibiotic therapy and histological confirmation of bone infection.
Treatment Strategies for a Diabetic Foot Infection
Antibiotic Therapy
Appropriate antibiotic selection depends on infection severity, suspected organisms, and patient-specific factors:
Empiric Therapy: Initial treatment typically covers common pathogens including Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus species, and gram-negative bacteria. For severe infections, we provide broad-spectrum coverage until culture results guide more targeted therapy.
Duration: Treatment length varies based on infection severity and bone involvement. Soft tissue infections may require 1-2 weeks of antibiotics, while osteomyelitis often demands 6 weeks or more of targeted antibiotic therapy.
Delivery Method: Mild infections usually respond to oral antibiotics, while moderate to severe cases require intravenous administration, either in the hospital or through home healthcare services.
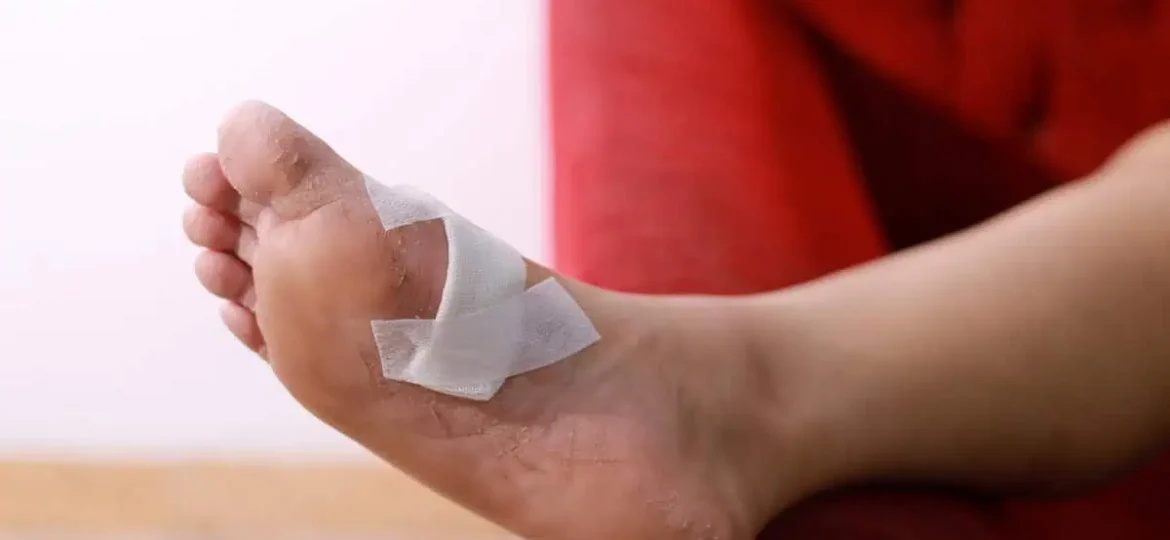
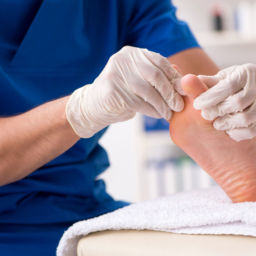
Wound Care Management
Proper wound care forms the foundation of successful treatment:
Debridement: Removing dead tissue, callus, and necrotic material creates a clean wound bed that promotes wound healing. This procedure, performed at our offices, improves antibiotic penetration and allows for better assessment of infection extent.
Dressing Selection: We choose wound dressings based on drainage amount, infection status, and healing stage. Options range from antimicrobial dressings for infected wounds to advanced biologics for promoting tissue regeneration.
Moisture Balance: Maintaining appropriate moisture levels—neither too wet nor too dry—optimizes the healing environment and prevents further tissue damage.
Offloading and Pressure Reduction
Reducing pressure on diabetic foot ulcers accelerates healing significantly:
Total Contact Casting: This gold-standard offloading device distributes pressure evenly across the foot, protecting the wound while allowing limited mobility.
Removable Cast Walkers: These provide good offloading when patients comply with wearing them consistently. However, compliance can be challenging, so our team emphasizes education about proper use.
Surgical Shoes and Custom Orthotics: For less severe ulcers or during the later healing stages, specialized footwear with custom insoles reduces pressure on vulnerable areas.
Surgical Interventions
Some infections require surgical treatment:
Incision and Drainage: Abscesses and deep pockets of infection need surgical drainage to remove infected material and allow proper wound healing.
Debridement: Extensive surgical debridement may be necessary for severe infections, removing all infected and non-viable tissue.
Bone Resection: When osteomyelitis is present, removing infected bone may be necessary. In some cases, this can be accomplished through minimally invasive techniques, while severe cases may require more extensive procedures.
Amputation: As a last resort when infection threatens life or cannot be controlled, amputation may be necessary. Our goal is always limb salvage, but patient safety takes priority.
Addressing Contributing Factors for a Diabetic Foot Infection
Blood Sugar Management
Controlling blood glucose levels is fundamental to infection treatment and prevention. High blood sugar impairs immune function and wound healing while promoting bacterial growth. Our podiatrists work closely with patients’ endocrinologists or primary care physicians to optimize diabetes management during treatment.
Vascular Assessment and Intervention
Patients with peripheral arterial disease may require vascular evaluation. Our practice collaborates with vascular surgeons who can perform interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery to restore blood flow, dramatically improving healing potential and treatment outcomes.
Nutritional Support
Proper nutrition supports immune function and tissue repair. Adequate protein intake, vitamin supplementation (particularly vitamins A and C), and overall caloric sufficiency help the body fight infection and heal wounds effectively.
Prevention: Your Best Defense
Preventing diabetic foot infections is far easier than treating them. Our team recommends this comprehensive prevention strategy:
Daily Foot Care Routine:
- Inspect your feet every day, using a mirror for the bottom and back of your feet
- Wash feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap
- Dry thoroughly, especially between toes
- Apply moisturizer to prevent dry, cracked skin, but avoid it between toes
- Never walk barefoot, even indoors
Proper Footwear:
- Wear shoes that fit properly with adequate room for toes
- Check inside shoes before wearing for foreign objects or rough spots
- Choose breathable materials that reduce moisture accumulation
- Consider diabetic shoes if you have foot deformities or previous ulcers
Professional Foot Care:
- Schedule regular podiatric examinations every 3-6 months
- Have corns, calluses, and nails trimmed professionally
- Address foot deformities before they cause problems
- Get custom orthotics if biomechanical issues are present
Blood Sugar Control:
- Maintain HbA1c levels as close to target as safely possible
- Monitor blood sugar regularly and adjust medications as directed
- Follow dietary recommendations from your healthcare team
- Exercise regularly within your capabilities
Risk Factor Management:
- Don’t smoke, as it severely impairs circulation
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Address any injuries immediately, no matter how minor
- Manage stress, which can affect blood sugar levels
When to Seek Immediate Care for a Diabetic Foot Infection
Contact any of our convenient locations or seek emergency care immediately if you experience:
- Any open wound on your foot, regardless of size
- Redness or warmth spreading from a wound
- Drainage, pus, or foul odor from your foot
- Fever accompanied by foot symptoms
- Black or darkened tissue on your foot
- Sudden increase in pain or swelling
- A puncture wound or injury that breaks the skin
Remember, with peripheral neuropathy, the absence of pain does not mean the absence of serious problems. Trust your eyes more than your nerve sensation.
Long-Term Outlook and Prognosis
The prognosis for diabetic foot infections depends on several factors: infection severity at presentation, blood sugar control, vascular status, compliance with treatment, and overall health status. Early intervention dramatically improves outcomes.
According to current research, appropriate treatment can heal most diabetic foot infections without major complications. However, patients who have had one diabetic foot ulcer face approximately a 40% risk of recurrence within one year and up to 65% risk within five years, making ongoing prevention efforts essential.
Our Commitment to Your Foot Health
At Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, our team of experienced podiatrists across multiple locations understands that managing diabetic foot infections requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach. With decades of combined experience treating patients with diabetic foot infections, from initial diagnosis through complete healing and prevention planning, we provide consistent, high-quality care at every office.
We utilize advanced diagnostic tools, evidence-based treatment protocols aligned with Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines, and the latest wound care technologies. Our collaborative approach involves working closely with your endocrinologist, primary care physician, vascular surgeon, and other specialists to ensure coordinated care.
Don’t wait until a minor problem becomes a serious threat. If you have diabetes, schedule your preventive foot examination at one of our convenient locations today. If you’re experiencing any signs of foot infection, contact the office nearest you immediately. Early intervention is your best protection against serious complications.
Living with diabetes requires vigilance, but with proper foot care, regular professional monitoring, and prompt attention to any concerns, you can maintain healthy feet and prevent infections. Our team is here to partner with you every step of the way, providing expert guidance, comprehensive treatment, and compassionate care at a location convenient for you.
Your feet carry you through life—let us help you keep them healthy and infection-free.
About the Practice: Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, LLC features a team of board-certified podiatrists with over 50 years of combined experience serving patients across multiple locations. Our practice specializes in diabetic foot care and stays current with the latest research and treatment protocols to provide evidence-based care that produces optimal outcomes. Find a location near you to schedule your appointment today.

 Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach
Comprehensive Diagnostic Approach