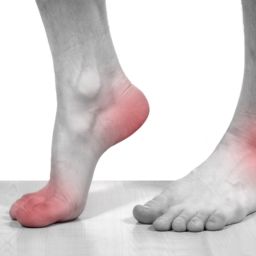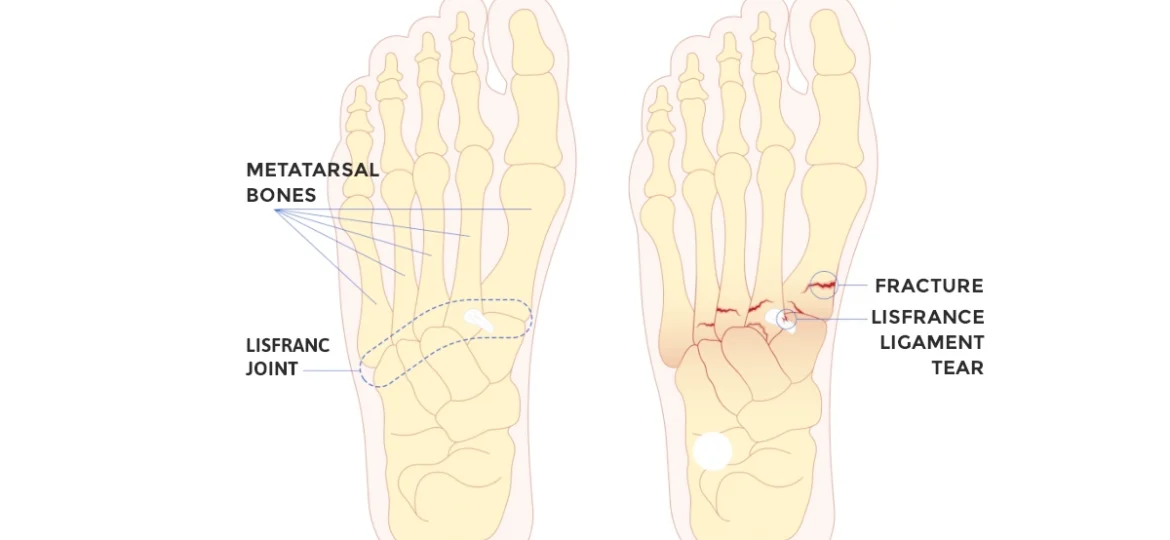
Lisfranc injuries are complex conditions affecting the midfoot, specifically the joint complex includes the tarsometatarsal joints, metatarsal and tarsal bones, as well as the vital Lisfranc ligament that stabilizes these structures.
Detailed anatomy of the Lisfranc joint complex and its significance
The Lisfranc joint complex includes the tarsometatarsal joints, metatarsal and tarsal bones, as well as the vital Lisfranc ligament that stabilizes these structures. This ligament connects the medial cuneiform bone to the base of the second metatarsal, providing structural stability and facilitating weight-bearing movements. Damage to this intricate structure can severely affect foot function and mobility.
Explaining the different types of Lisfranc injuries and their impacts
Injuries to the Lisfranc joint can range from minor sprains to severe fractures and dislocations, each requiring different treatment approaches:
- Sprains: These involve partial tears or overstretching of the soft tissues, including the Lisfranc ligament. Though less severe, sprains can still cause significant discomfort and instability.
- Fractures: Lisfranc fractures occur when one or more bones in the joint complex break, often resulting from direct trauma or excessive force.
- Fracture-Dislocations: This severe condition involves both fractures and displacement of the tarsometatarsal joints, leading to misalignment that usually requires surgical intervention.
Lisfranc injuries frequently result from high-energy trauma, such as car accidents, falls from significant heights, or direct impacts during sports. Football players and athletes in high-impact sports are particularly susceptible, as rapid directional changes and twisting motions can overload the midfoot.
Recognizing key symptoms of a Lisfranc injury for timely action
Prompt identification of Lisfranc injuries is critical to avoid long-term complications. Common symptoms include:
- Severe swelling and bruising, often on both the top and bottom of the foot.
- Intense pain, especially when putting weight on the injured foot.
- Difficulty in walking or maintaining balance.
- Visible deformity in cases of fracture-dislocations.
Diagnostic tools and procedures to confirm Lisfranc injuries
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Physicians use a combination of physical exams and advanced imaging tests to locate a lisfranc injury fracture:
- Physical Examination:Identifying tenderness, swelling, and bruising in the midfoot area.
- X-rays: Detecting fractures and any misalignment of the joints.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Providing detailed views of soft tissue damage, such as Lisfranc ligament tears.
- CT Scan: Offering a comprehensive understanding of complex fractures and joint displacement.
Non-surgical treatment options for mild Lisfranc injuries
For minor injuries with no significant displacement, conservative treatment is often sufficient:
- Immobilizing the foot with a cast or boot to restrict movement.
- Strictly avoiding weight-bearing activities for several weeks.
- Gradually reintroducing light activity under medical supervision to ensure proper healing.
Surgical interventions for severe Lisfranc fractures and dislocations
Severe lisfranc injuries frequently require surgical correction to restore alignment and function. The two primary surgical approaches are:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): Surgeons realign the fractured bones (open reduction) and stabilize them with screws or plates (internal fixation).
- Fusion Surgery: For extensive damage, fusion permanently joins the affected bones, eliminating painful movement but sacrificing some flexibility.
Comprehensive recovery process after a Lisfranc injury fracture
Recovery from a lisfranc injury fracture is a gradual process that demands patience and adherence to a structured plan:
- Post-Treatment Rest: Patients often remain non-weight-bearing for 6-8 weeks post-treatment to allow healing.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Physical therapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and coordination in the affected foot.
- Monitoring Long-Term Outcomes: Even after healing, some patients may experience residual stiffness or arthritis in the Lisfranc joint complex.
Practical tips to prevent Lisfranc injuries and protect foot health
Prevention strategies can significantly reduce the risk of a lisfranc injury fracture:
- Wear well-fitted, supportive footwear designed for specific activities.
- Strengthen foot and ankle muscles through targeted exercises.
- Avoid activities that place excessive stress on the midfoot, especially without proper preparation.
Recognizing when to consult a doctor for foot injuries
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or difficulty bearing weight after a foot injury, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can prevent complications such as chronic pain, joint instability, or arthritis in the Lisfranc joint complex.
Addressing Lisfranc injury Fracture for optimal recovery
Lisfranc injuries, whether mild sprains or severe fracture dislocations, require timely diagnosis and personalized treatment. Advanced surgical techniques like Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) and fusion surgery, combined with diligent rehabilitation, offer the best outcomes for restoring foot function. Protecting your midfoot health ensures mobility and quality of life – don’t hesitate to seek professional care if you suspect a lisfranc injury fracture.
At Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, our team of experts is dedicated to providing comprehensive care tailored to your specific needs. Book an appointment today to receive a thorough evaluation and the best treatment options to get you back on your feet with confidence.