Leg cramps, also known as “charley horses,” are abrupt and excruciating muscle contractions, frequently manifesting in the calf muscles. These episodes, notorious for their unpredictability, can disrupt even the most routine daily activities, inflicting considerable discomfort upon patients.
An ingrown toenail, also known as onychocryptosis, is a common condition where the border of a toenail does not grow over the skin but into it. It most commonly affects the big toe but can occur in other toes as well. This condition can cause pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
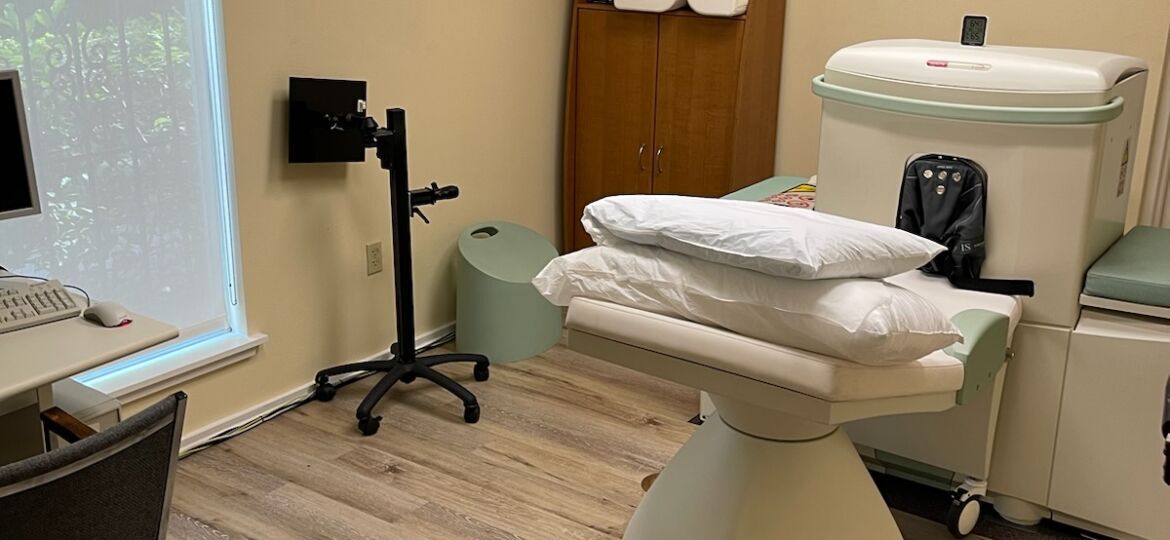
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful medical imaging technique that has revolutionized the way podiatrists diagnose and treat various foot and ankle conditions. Traditionally, podiatrists would rely on X-rays, ultrasounds, and CT scans to assess musculoskeletal issues, but MRI offers unparalleled detail and accuracy. The integration of MRI technology into podiatry practices has provided numerous benefits, with the introduction of in-office MRI machines further enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes. This article delves into the usage of MRI in podiatry and explores the advantages of having an in-office MRI machine.
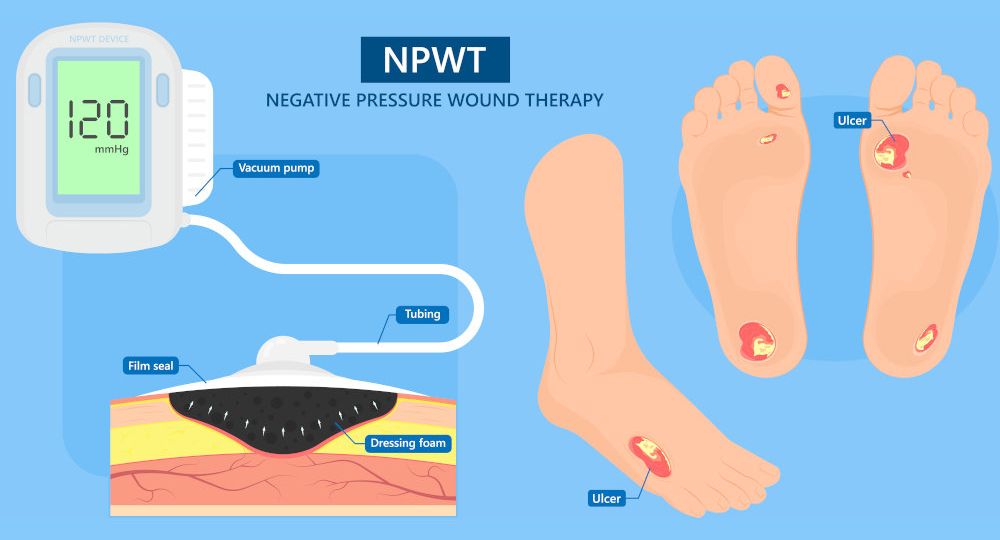
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) is a medical technique used to promote wound healing. It involves applying controlled negative pressure (suction) to a wound through a specialized dressing and sealed system. This therapy helps in several ways: it removes excess fluid, reduces swelling, and enhances blood flow to the wound area, which can aid in tissue regeneration. NPWT is particularly beneficial for chronic or complex wounds, diabetic ulcers, and post-surgical incisions. The controlled vacuum created by NPWT assists in reducing bacterial contamination, speeding up the healing process, and promoting healthy tissue formation. It’s often utilized under the guidance of medical professionals for optimal wound care.
An ingrown toenail, also known as onychocryptosis, is a common condition where the border of a toenail does not grow over the skin but into it. It most commonly affects the big toe but can occur in other toes as well. This condition can cause pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
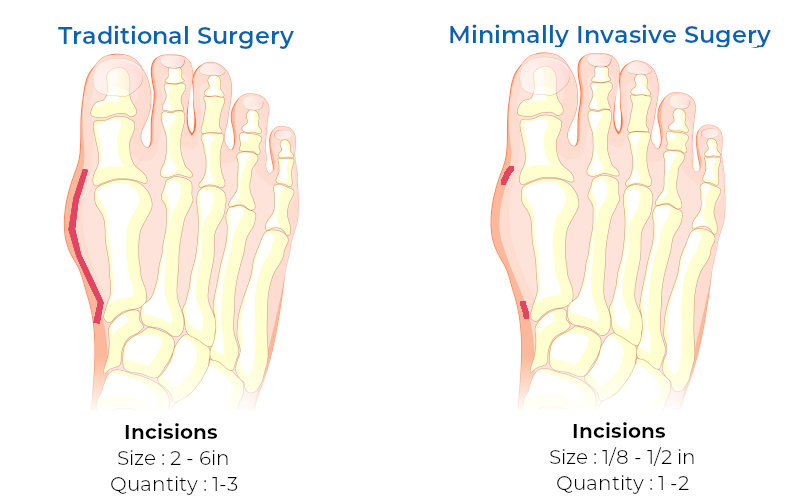
When it comes to foot health, we often underestimate its importance until we’re faced with discomfort or pain. Whether it’s bunions, hammertoes, stress fractures, or plantar fasciitis, these conditions can hinder our daily lives and keep us from enjoying our favorite activities.
Tarsal sinus syndrome, also known as sinus tarsi syndrome, is a relatively rare condition characterized by pain and instability in the foot’s tarsal sinus region. The tarsal sinus is a small tunnel-like structure located on the outside of the ankle between the talus and calcaneus bones.
Ankle impingement refers to a condition characterized by pain and limited range of motion in the ankle joint. It occurs when there is compression or pinching of the soft tissues or bone structures within the ankle during certain movements. This can lead to discomfort and inflammation in the joint.
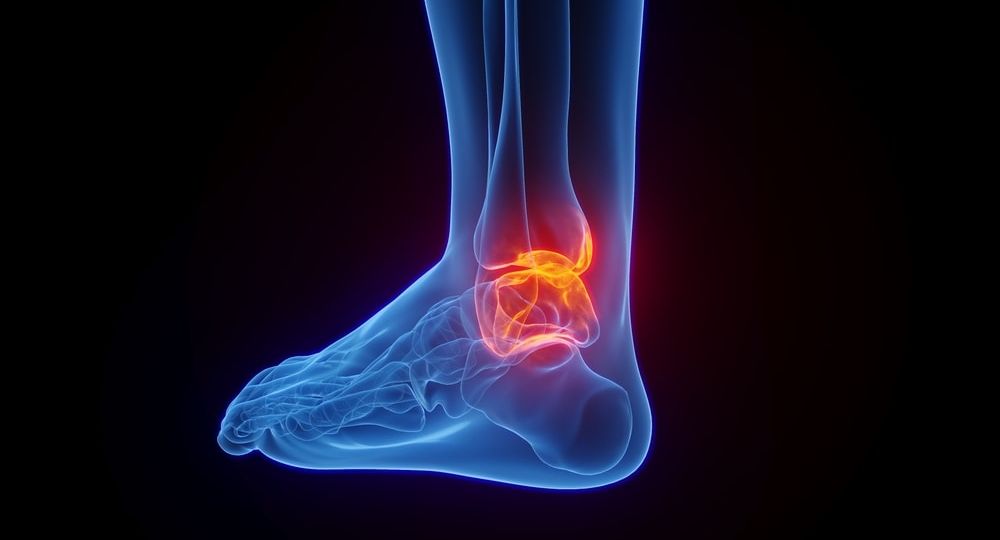
A torn ankle ligament is a common injury that occurs when the ligaments in the ankle are stretched or torn due to a sudden twisting or rolling movement. The ankle joint is supported by a network of ligaments that help to keep it stable during movement, and when these ligaments are injured, it can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. Torn ankle ligaments are most commonly caused by activities that involve sudden changes in direction, such as sports or running on uneven surfaces.
Foot injuries can be a serious concern for people with diabetes. Diabetic heel pain can occur at any age but is more common in older adults who have had diabetes for a longer period of time.