Baxter’s nerve entrapment or baxter’s neuropathy, often overshadowed by the more commonly discussed plantar fasciitis, emerges as a pivotal culprit behind chronic heel pain. This condition, related to the entrapment of the inferior calcaneal nerve, a branch of the lateral plantar nerve, demands precise diagnosis and treatment to alleviate the distress it causes.
Understanding Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
The nerve entrapment typically occurs near the medial calcaneal tuberosity, where the nerve originates from the lateral plantar nerve. It is crucial to understand the anatomy involved, including the relationship of the nerve with the abductor hallucis muscle, the flexor digitorum brevis, the quadratus plantae muscles, and the long plantar ligament, to grasp why certain treatments are effective.
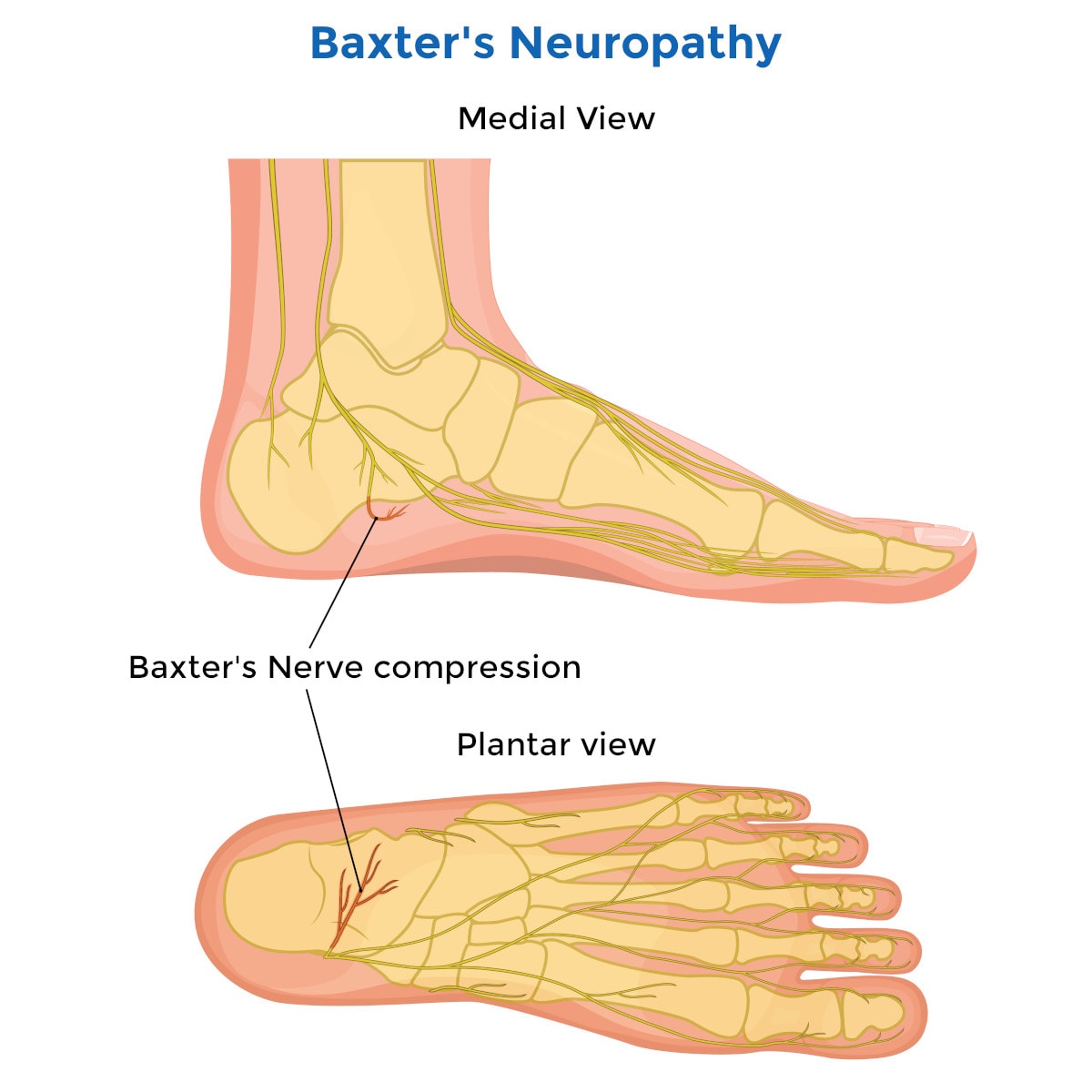 What are the Symptoms and Diagnosis?
What are the Symptoms and Diagnosis?
Patients report plantar heel pain that mimics symptoms of plantar fasciitis but often lacks the classic signs of that condition. The pain, concentrated around the heel and possibly involving the abductor digit minimi muscle, requires careful evaluation to diagnose accurately, distinguishing it from other heel pain causes.
Diving into Causes and Risk Factors for Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment
The causes and risk factors underlying nerve entrapment are distinct and multifaceted, including anatomical, physiological, and lifestyle elements.
- Anatomical Predisposition: One of the primary causes of nerve entrapment is the anatomical structure and variations in the foot. The Baxter’s nerve entrapment can occur due to a tight abductor hallucis muscle fascia or because of its proximity to the medial calcaneal tuberosity. Individuals with an abnormally thick or tight fascia of the lateral plantar nerve are at a higher risk.
- Heel Spurs and Plantar Fasciitis: While Baxter’s nerve entrapment is a separate condition, the presence of heel spurs and symptoms of plantar fasciitis can exacerbate the risk of nerve entrapment. Heel spurs, bony growths on the underside of the heel bone, can put additional pressure on the Baxter’s nerve, leading to entrapment.
- Long Plantar Ligament Strain: Activities that strain the long plantar ligament, such as prolonged standing, running, or other high-impact sports, can increase the risk of developing nerve entrapment. The strain can cause inflammation and swelling in the area, affecting the nerve.
- Footwear and Lifestyle Factors: Inappropriate footwear that does not provide adequate support to the arch and heel can lead to or exacerbate nerve entrapment. Occupations that require extended periods on one’s feet or involve heavy lifting can also be contributing factors.
- Systemic Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and obesity can increase the susceptibility, due to the additional stress placed on the feet and the potential for nerve damage (neuropathy) associated with diabetes.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for preventing and treating the condition. It emphasizes the importance of comprehensive foot care, including selecting proper footwear, managing underlying health conditions, and moderating activities that place excessive strain on the feet.
What are the Treatment Options for Baxter’s nerve entrapment?
Effective management involves a multifaceted approach, including both non-surgical and surgical options, tailored to the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in alleviating symptoms and preventing further complications.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Conservative Management: Initial treatment often focuses on reducing inflammation and alleviating pain without surgery. This may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol), along with the use of anti-inflammatory medications.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches designed by a physical therapist can help relieve pressure on the entrapped nerve. Techniques may focus on strengthening and stretching the abductor hallucis, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digitorum brevis, and the surrounding muscles to reduce tension and inflammation.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotics or supportive footwear can be effective in redistributing pressure away from the affected area, providing relief from symptoms. Proper arch support can also prevent further entrapment.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections around the area of nerve entrapment can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation. However, this treatment is usually considered temporary and part of a broader management strategy.
Surgical Treatments
When non-surgical treatments fail to provide adequate relief or in cases of severe entrapment, surgical intervention may be considered.
- Nerve Release Surgery: This procedure involves surgically releasing the entrapped nerve to alleviate pressure. The surgeon may remove or release the fascia of the lateral plantar nerve or other structures that are compressing the nerve.
- Removal of Heel Spurs: If heel spurs are contributing to the entrapment, they may be surgically removed to reduce pressure on the nerve.
- Neurolysis: This involves the decompression of the nerve by removing scar tissue or any other compressive elements around the nerve.
The choice between non-surgical and surgical treatment options depends on several factors, including the duration and severity of symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and their response to initial treatments.
The surgeons at Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists work closely with patients to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment plan, ensuring that each patient receives personalized care tailored to their unique situation.
Patients need to understand that recovery from Baxter’s nerve entrapment varies, and a comprehensive approach involving professional medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and potentially surgery, offers the best chance for a successful outcome.
How Can You Prevent or Manage this Condition?
Preventing Baxter’s nerve entrapment and managing its symptoms effectively requires a proactive approach to foot health, incorporating lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and early intervention. These strategies not only aim to reduce the risk of nerve entrapment but also to enhance overall foot and ankle well-being.
Prevention Strategies
- Proper Footwear: Choosing shoes that provide good arch support and cushioning can help distribute pressure evenly across the feet, reducing the risk of nerve entrapment. Avoiding high heels and tight-fitting shoes is also recommended.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: For individuals whose occupation requires extended periods of standing or walking, implementing ergonomic adjustments such as anti-fatigue mats and taking regular breaks to sit and elevate the feet can alleviate prolonged pressure on the feet.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes the stress on the feet and can prevent a range of foot problems, including nerve entrapment.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises that strengthen the foot and ankle muscles can improve foot mechanics and prevent conditions that lead to nerve entrapment. Stretching exercises for the calf muscles can also relieve tension in the foot.
Management Tips
- Early Intervention: At the first sign of chronic heel pain, consulting with a foot and ankle specialist can prevent the progression of symptoms and reduce the likelihood of requiring surgical intervention.
- Custom Orthotics: For individuals prone to foot problems, custom orthotic devices designed to address specific foot structure issues can prevent the recurrence of nerve entrapment.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular follow-ups with a podiatrist can help monitor the health of your feet and catch any signs of nerve entrapment early. This is especially important for people with diabetes or other conditions that affect foot health.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporating foot health into daily routines, such as performing foot stretches, choosing appropriate footwear for activities, and managing any underlying health conditions, can significantly impact the prevention and management of the nerve entrapment.
By adopting these preventative measures and management strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing Baxter’s nerve entrapment and ensure their feet remain healthy and pain-free. Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists are committed to providing patients with the knowledge and resources necessary to take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal foot health.
In Summary…
Through understanding the intricacies of this condition—from its causes and symptoms to the comprehensive treatment options available—patients can navigate their path to recovery with confidence.
At Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, we emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Whether through conservative management techniques or surgical intervention, our goal is to alleviate pain and restore functionality, ensuring our patients can return to their daily routines without discomfort.
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing foot health. By adopting lifestyle modifications such as wearing proper footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating foot-strengthening exercises, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing Baxter’s nerve entrapment. Regular check-ups with a foot and ankle specialist are vital to catching potential issues early and keeping your feet healthy and pain-free.
The feet are the essential components that move our body. Taking proactive steps to care for them not only prevents conditions like Baxter’s nerve entrapment but also contributes to your overall well-being. If you’re experiencing persistent heel pain, don’t hesitate to reach out to Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists. Together, we can take the necessary steps towards achieving optimal foot health and improving the quality of your life.
Call Our Foot And Ankle Specialists today!
We have locations in the South East and West Coast of Florida to serve you better. If you are seeking a foot and ankle doctor in Brandon consider booking an appointment with our certified doctors.
Please contact us today at 855-550-3338 or send us a message to schedule a consultation.