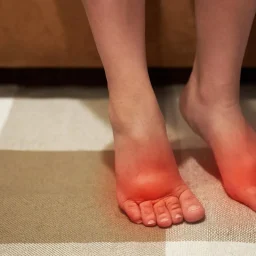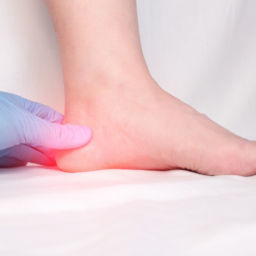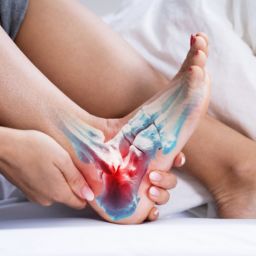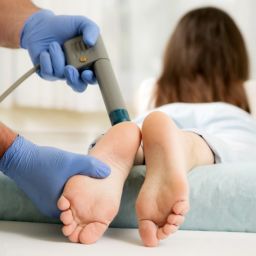
Foot injuries can be a serious concern for people with diabetes. Diabetic heel pain can occur at any age but is more common in older adults who have had diabetes for a longer period of time. As a person with diabetes gets older, they may be more likely to experience complications such as peripheral neuropathy or poor circulation, which can lead to diabetic heel pain. Additionally, people who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels for an extended period of time may also be at increased risk for developing diabetic foot problems, including heel pain.
- According to the American Diabetes Association, about 15% of people with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer at some point in their lives, which can be a precursor to more serious complications such as amputation.
- A study published in the Journal of Foot and Ankle Research found that up to 25% of people with diabetes experience foot pain, with heel pain being one of the most common types of foot pain reported.
- Another study published in the journal Diabetes Care found that about 10% of people with diabetes experience foot pain specifically related to plantar fasciitis, a condition that can cause the arch of the foot and heel to experience soreness or throbbing discomfort
While there is limited data specifically on diabetic heel pain, foot problems are a common complication of diabetes, and heel pain can be a symptom of a range of conditions associated with diabetic foot problems.
To protect your feet, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including managing your blood glucose levels. Increased sugar levels in the blood can worsen your risk of developing foot issues, including plantar fasciitis, a common condition caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot.
To prevent foot injuries, it is important to take good care of your feet. This includes wearing proper footwear that fits well and provides support, avoiding going barefoot, and regularly inspecting your feet for any cuts, sores, or other signs of injury. If you do notice any issues, it is important to seek prompt medical attention.
What Are The Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain in the heel or arch of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a ribbon of tissue that stretches along the base of the foot, becomes inflamed or irritated. The symptoms of plantar fasciitis can vary, but commonly include:
- Pain in the heel or arch of the foot, which is often worse in the morning or after prolonged periods of standing or walking.
- Stiffness or tightness in the foot, which may make it difficult to move or walk.
- Swelling or redness in the affected area.
- Aching or burning in the foot, which may be more pronounced at the end of the day.
- Acute penetrating pain in the heel or arch of the foot.
If left untreated, plantar fasciitis can become a chronic condition and lead to more severe pain and discomfort. It can also make it difficult to engage in everyday activities, such as walking or running.
Choices for the treatment of plantar fasciitis may include rest, ice, stretching, and physical therapy. In some cases, medication or corticosteroid injections may also be recommended to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. With proper treatment, most people with plantar fasciitis can recover fully and return to their normal activities.
How Does Peripheral Neuropathy Affect Heel Pain?
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that affects the nerves in the feet and other parts of the body. It can cause a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, burning, or shooting pains. It can also cause muscle weakness and loss of coordination, making it difficult to walk or perform everyday activities.
For people with diabetes, peripheral neuropathy can be a particular concern, as high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves in the feet and reduce blood flow to the area. This can lead to diabetic foot pain, as well as an increased risk of infections and other foot problems.
To care for your feet when you have peripheral neuropathy, it is important to check your feet regularly for any cuts, sores, or other signs of injury. You should also wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate support, avoiding high heels or shoes that are too tight or narrow. People with type 2 diabetes should work with their healthcare team to manage their blood sugar levels, as this can help reduce the risk of nerve damage and other complications.
Regular exercise can also be helpful for maintaining blood flow to the feet and reducing the risk of complications associated with peripheral neuropathy. By taking good care of your feet and working with your healthcare team, you can manage the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and reduce the risk of serious foot problems.
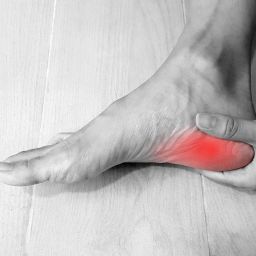
How Can You Treat Diabetic Heel Pain?
Diabetic heel pain can be a particularly challenging condition to treat, as it can be caused by a range of factors, including peripheral neuropathy, poor circulation, and foot deformities such as hammer toes. Treatment options for diabetic heel pain may include:
- Wearing proper footwear: Properly fitting shoes that provide good support and cushioning can help reduce pressure on the heels and alleviate pain.
- Custom orthotics: Custom-made shoe inserts can help distribute weight more evenly across the foot, reducing pressure on the heels.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or topical creams may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct underlying foot deformities or other issues that are contributing to heel pain.
It is also important to manage blood glucose levels which can exacerbate diabetic heel pain. Regular foot exams are also important for identifying any signs of foot problems, such as ulcers or infections, that can cause or worsen heel pain.
The best approach to treating diabetic heel pain is a comprehensive one, involving a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and other interventions tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
Why should you visit Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists?
Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists is an excellent choice for patients with diabetic feet because they offer specialized care and expertise in the management of foot problems associated with diabetes.
At any of our clinics, a team of experienced podiatrists are well-versed in the latest techniques and treatments for managing diabetic foot problems, including diabetic neuropathy, plantar fasciitis, and other conditions that can cause heel pain.
By visiting Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists for diabetic foot care, patients can benefit from personalized treatment plans tailored to their individual needs, as well as regular foot exams to monitor for signs of foot problems or complications. They also offer custom-made orthotics and specialized footwear to help reduce pressure on the feet and prevent further damage.
Overall, by seeking care from a specialized foot and ankle clinic in boca raton like Certified Foot and Ankle Specialists, patients with diabetic feet can receive the highest quality care to help manage their condition and prevent serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is heel pain so common for people with diabetes?
In Florida’s warm climate, staying active is a way of life — but diabetes can make foot care tricky. High blood sugar can damage nerves (called peripheral neuropathy) and restrict blood flow, making your heels more vulnerable to pain, inflammation, and even serious injuries.
2. How does plantar fasciitis relate to diabetic heel pain?
Plantar fasciitis, or inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot, is a big culprit. If you have diabetes, this tissue can weaken, especially if you’re often on your feet — whether you’re walking the beach or cruising a theme park.
3. What are the early signs of diabetic heel problems I should watch for?
Keep an eye out for morning heel pain, swelling, burning sensations, stiffness, or redness. If you’re in Florida’s hot and humid weather, always inspect your feet after a long day outside, since moisture can make problems worse.
4. What’s the best way to treat heel pain if I have diabetes?
Start with supportive, cushioned shoes (goodbye, flip-flops!) and use ice to ease inflammation. Stretching exercises, blood sugar management, and sometimes physical therapy are key. Always seek a podiatrist’s help if the pain sticks around — better safe than sorry under the Florida sun!
5. How can I prevent diabetic heel pain while staying active in Florida?
Stick to breathable, supportive footwear, avoid going barefoot (even at home or the beach), and check your feet daily for any sores or redness. Managing your blood sugar and staying active with low-impact exercises like swimming can also keep heel pain at bay.