Overview
A broken ankle, or fractured ankle, is one of the most common injuries of the lower extremity. This injury is more common in middle aged women and young men, as well as athletes of all ages. Treatment for a broken ankle depends on which bones are broken, if there is injury to other surrounding structures, and the severity of the injury. When the fracture is serious, it may require surgical intervention. It can take several months to recover from an broken ankle fracture.
What is a broken ankle?
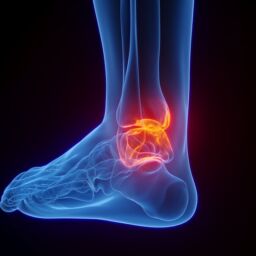
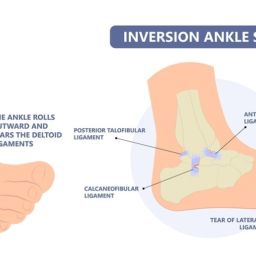
Your ankle is made up of three bones: the tibia, the fibula, and the talus. The tibia and fibula are in your lower leg, while your talus is a bone in your foot. Your talus acts as the connection between your leg and your foot. When either the tibia or fibula suffer an injury that causes a crack or break in the bone, you have suffered a broken ankle.
You can break one or more bones in your ankle at the same time. The bony prominence on the inner area of your ankle is called the medial malleolus and is a part of the tibia. You can also fracture the posterior malleolus, which is on the back side of the tibia. The fibula ends in the lateral malleolus, located on the outer side of the ankle.
What are the types of broken ankles?
The severity of a broken ankle depends on the parts of the tibia and fibula that are fractured, how many bones are involved, and if the bones are in the correct position.
If only one fracture is present, most often it is the lateral malleolus. If two fractures are present, it is called bimalleolar fracture, usually involving the lateral and medial malleolus. If three fractures are present, it is called a trimalleolar fracture, involving the lateral malleolus, medial malleolus, and posterior malleolus.
If an ankle fracture has occurred but the bones are not shifted out of place, this is called a nondisplaced fracture. These types of fractures do not typically require surgery. If the bones have moved out of place, this is called a displaced fracture. These types of fractures need to be put back into the correct position, usually with surgery. If there is a cut or wound on your ankle, possibly with bone sticking out of the skin, this is called an open fracture. This is very serious and an emergency because an infection can occur. You need to see a podiatrist right away so the wound can be cleaned, and the fracture can be fixed, again, typically with surgery.
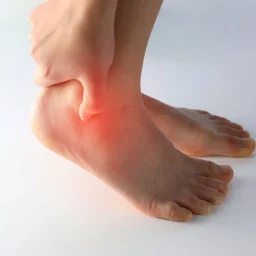
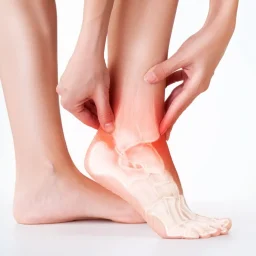
How do I know if my ankle is broken?
Ankle fractures can occur due to a trip and fall, rolling or twisting motion, or from a motorcycle or car accident. Signs that you have a broken ankle can include the following:
- You are unable to walk or bear weight on the injured ankle or foot.
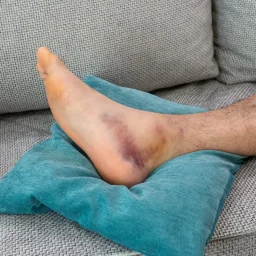
- There is swelling to the ankle or foot.
- There is bruising to the ankle or foot.
- There is pain with touching or moving the ankle.
More serious injuries can cause deformity of the ankle, meaning it is bent out of shape. You may also experience numbness of the foot. It is important to see your podiatrist to ensure diagnosis of an ankle fracture, assuring complete recovery and to restore function and mobility as fast as possible.
What will a podiatrist do for my broken ankle?
First, your podiatrist will do a thorough foot and ankle exam, checking for areas of pain, bruising, and swelling. Next, they will check your pulses for blood flow, and your sensation to assess for nerve injury.
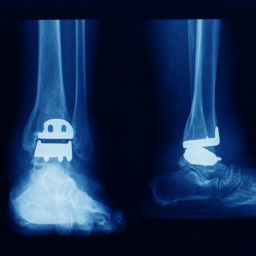
Your podiatrist will take X-rays of your ankle to visualize the bones that are broken or out of place. Because fractures of your foot or leg can occur alongside fractures of your ankle, your podiatrist may also take X-rays of both your foot and leg to assure you that no other injuries have occurred. A special X-ray called a stress X-ray may also be needed if your podiatrist is worried about injury to your syndesmosis. An MRI can be useful to evaluate injury to tendons and ligaments that are not easily visualized with stress X-ray. Sometimes a CT scan is needed to further evaluate the severity of the broken ankle.
What are the treatment options for my broken ankle?
Once the bones that are broken are identified, a podiatrist will analyze whether the fracture is nondisplaced or displaced. If there is no shifting of the broken ankle bones, a conservative (non-surgical) approach can be used. These include RICE therapy:
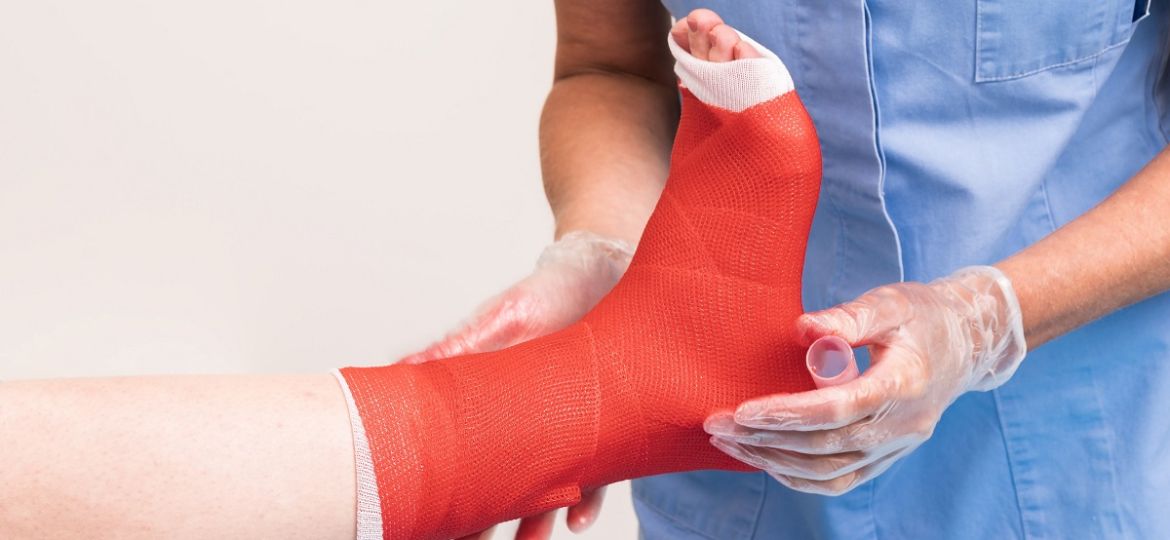
- Rest: Limited activity and weight on the broken ankle are essential to prevent the bones from shifting. You may be placed in an immobilizing device such as fiberglass cast or a surgical boot for stabilization of the fracture.
- Ice: Icing your broken ankle 15 to 20 minutes every one to two hours with an ice pack or bag of peas will help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Compression: A compression dressing or ACE wrap will be applied to your lower leg to reduce swelling, which will help alleviate pain and heal bruising.
- Elevation: Keeping your broken ankle elevated above the level of your heart, typically on 2 pillows, will reduce swelling and pain.
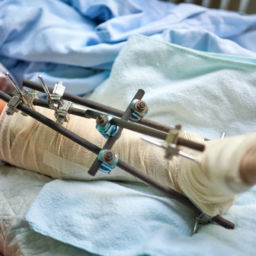
If the bone fragments are displaced, are in multiple bone fragments, or are considered unstable, the ankle fracture will require surgery. Podiatrists are specially trained in broken ankle fracture repair treatment. Surgical treatment of a broken ankle is dependent on the bones that are broken. Hardware including screws and/or plates and other devices are used to realign the fractured bones into correct position and provide temporary strength and stability while the broken bones are healing. Your skin will have stitches to hold the incision together.
What is the recovery like from a broken ankle?
On average, broken bones take about four to six weeks to heal. If ligaments or other soft tissue injuries have occurred, recovery time can increase. Regardless of treatment type, pain management can include icing, elevation, and oral pain medication. Oral pain medication includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs) and over-the-counter pain medication such as acetaminophen (Tylenol). These are used to reduce your need for opioids.
If conservative (nonsurgical) treatment has been used, you may be told that you can bear weight in an immobilization boot while the bones heal. You may also be given crutches or a knee scooter to reduce weight bearing, depending on the type of ankle fracture.
If broken ankle fracture treatment with surgery is needed, you are typically not weight bearing for four to six weeks until bone healing is achieved. Around two weeks after surgery, stiches are removed from the incision.
Whether you have had surgery or not, repeated X-rays of your ankle will be used to monitor bone healing. Once healing in the bones is seen, rehabilitation will be recommended for complete recovery and regaining full function of your broken ankle. Wait for your podiatrist to tell you when you can start to put weight on your ankle to prevent shifting of the ankle fracture or failure of the surgery. Physical therapy may be needed.
What are possible complications after an ankle fracture?
Due to the different types of anatomy that can be injured with a broken ankle, there are a variety of complications that may occur after an ankle fracture. In general, stiffness and swelling of the ankle joint are the most common. These can occur for months to years after the initial injury but can be prevented and relieved with appropriate rehabilitation and elevation.
Specific to broken ankle fracture treatment with surgery, risks and complications include:
- Infection
- Problems with incision healing
- Damage to blood vessel, nerves, or tendons
- Problems with hardware used to repair your ankle
- Arthritis
Final Comments
If you believe you or a loved one has suffered a broken ankle, contact your podiatrist today for an examination. They can help to diagnose, treat, and recover from a broken ankle.
Dr. Purtuc is your local foot doctor in Vero Beach, Florida. A board certified podiatrist who specializes in foot and ankle surgery with over 10 years of experience. If you have any questions, feel free to send us an email or call our clinical office.